Endometrial neoplasm is a malignant disease that develops as tumor or cancer affects the endometrium which is the lining of the uterus. Among the endometrial cancers, uterine cancer is one of the common types. Endometrial cancer is usually detected early in its development with the presence of abnormal vaginal discharge. This cancer can be fatal if left untreated. It can also spread to the other parts of the body such as lymph nodes, ovaries and fallopian tubes. This generally affects the postmenopausal women between the ages of 50 – 70 and is uncommon under the age of 45.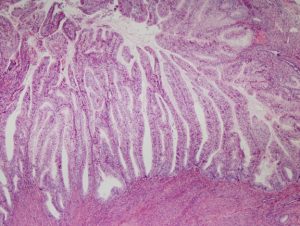
Causes
The growth and development of endometrium are based on the interaction of estrogen and progesterone receptors. The endometrium cells naturally stop multiplying when they are old or damaged, being replaced by healthy cells. The endometrial cancer is the result of these mature cells continuing to multiply without control. The exact cause of this disorder is unknown but the excess of estrogen in the body may play a role.
Symptoms
Around 90% of women affected by endometrial cancer tend to have unusual vaginal bleeding and spotting. The other associated symptoms include pelvic pain and weight loss.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of endometrial cancer usually involves a pelvic or trans-vaginal ultrasound. Endometrial tissues sampling may be required involving the procedure of either dilation and curettage (D&C) or endometrial biopsy. In the advanced form of cancer, a CT scan and MRI may be required to assess if cancer is spreading.
Treatment depends on the severity of cancer. Surgery to remove the uterus is generally recommended and the surgical removal of the uterus is called hysterectomy. In some cases hormone therapy will be administered for advanced endometrial cancer which may have spread beyond the uterus. This therapy involves elevating the progesterone level and to reduce the estrogen level in the body. After the surgery, radiation therapy may assist in controlling cancer reoccurrence.
Risk factors
The factors that influence the development of endometrial cancer are individuals taking estrogen replacement, being obese, use of birth control pills and polycystic ovarian syndrome. Other risk factors include diabetes, use of an intrauterine device, history of ovarian or breast cancer.



