Bjornstad syndrome is a rare inherited condition presented with hearing and hair problems. These individuals have the abnormal hair known as pili tori because of the twisted appearance of the hair strands under the microscope. The hair strands are usually brittle that breaks easily resulting in short hair that grows slowly. This hair abnormality may begin before the age of 2 and may be milder after puberty. The severity of the hearing varies among the affected individuals from a mild condition with the inability to hear certain sound frequencies to complete deafness. The exact prevalence of this syndrome is not known although it is evident in the general population around the globe.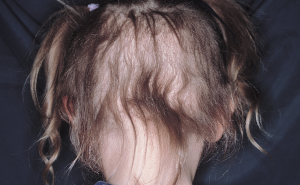
Causes
The mutation in the gene BCS1L is associated with the development of bjornstad syndrome. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern meaning the defective gene responsible for the same disorder is inherited from both the parents. The affected individual’s parents with the recessive disorder can each carry a defective gene but may not exhibit any of the symptoms associated with this condition.
Symptoms
Individuals affected with this syndrome usually have hair that is dry, fragile and coarse. When the hair strands are observed under the microscope, it gives a twisted appearance making them brittle and dry. This condition particularly affects the hair of the scalp, eyebrows and eyelashes although the hair strands in the other parts of the body appear normal. In some cases, a patchy hair loss may also be evident. In addition, these affected individuals have problems with hearing and deafness. This occurs with the inability of the auditory nerve to deliver the sound to the brain (sensorineural hearing loss). The hearing problem may be evident at the birth of the infant or may occur within the first year of the infant’s life. In addition, the sexual organs may also be affected resulting in delays with the secondary sexual development such as breast and hair growth.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis may be possible with the presence of twisted hair (pili torti) that is characteristic of bjornstad syndrome which may be evident at birth. The diagnosis can be confirmed by the microscopic observation of the hair strands. As this feature is common in bjornstad syndrome, the suspected cases should also be assessed for hearing problems using various hearing tests.
Treatment
The treatment may require the coordinated efforts of different medical specialists such as pediatricians, audiologist and dermatologist who may determine an effective treatment plan for the affected individual. The hair loss may require hair replacement therapies and hearing loss should be diagnosed early to ensure the children do not develop speech difficulties. The children with congenital hearing loss can benefit from special remedial educational services. Genetic counseling may also be supportive for the affected individual’s family.